|
|
||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x y z | #
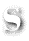
saddle-stitched:
A form of binding that uses staple-shaped wires through the gutter fold; also called saddle-wired.saddle-wired:
A form of binding that uses staple-shaped wires through the gutter fold; also called saddle-stitched.safelight:
A lamp used in a darkroom that doesn't affect sensitized materials.sales rep:
A person who presents new books to bookstores and takes orders for the books. Also called a book traveler, or traveler.sans serif:
A typeface without serifs.SASE:
Self-Addressed, Stamped Envelope. Required in any unsolicited material sent to book publishers so that the inquiring author will receive a response from the publisher.saturation:
A measure of the purity of a color, determined by the amount of gray it contains. The higher the gray level, the lower the saturation.scale:
To reduce or enlarge an image or a page proportionally.scaling:
The process of determining the amount an image should be reduced or enlarged to fit a specified area.scanner:
A device used to turn hardcopy output such as paper, slides, or transparencies into digital information for the purpose of manipulating and reproducing on the computer.screen frequency:
The number of lines per inch (LPI) or dots per inch (DPI) in a halftone screen.score (noun):
The indented line in a sheet of paper that makes it easier to fold.score (verb):
To indent a line in the paper that makes it easier to fold.screen:
Short for halftone screen. The reproduction of continuous-tone artwork, such as a photograph, by screening the image into dots of various sizes. When printed, the dots merge to give the illusion of continuous tone.screen angles:
The angles at which halftone screens are placed in order to avoid undesirable screen patterns, called moirés.screen ruling:
The number of lines or dots per inch in a halftone screen.screened print:
An image with a halftone screen made from a halftone negative or by diffusion transfer.scum:
An undesirable film of ink that prints in the non-image areas of a plate in offset lithography.search and replace:
The process of automatically locating a specific word or symbol in a word processing or page layout file and replacing it with another word or symbol.search engine:
A mechanism for finding things on the Internet. Popular search engines include Yahoo, Lycos, Alta Vista, and many others.second serial rights:
The right to publish a serialized version of a work after it has already been published.self cover:
A cover made from the same paper as the interior pages of the publication.self mailer:
A brochure that can be mailed as a standalone piece without the use of an envelope.semi-chemical pulp:
A combination of chemical and mechanical pulp used in papermaking.separation:
A film negative or positive to be used for each printing plate.serial:
A publication, such as a series of books, issued at regular intervals.serif:
The small strokes at the end of the main strokes of letterforms.server:
A computer or system of computers that archives and delivers digital files.service bureau:
An organization that provides output services to publishers and design shops in the form of high-resolution film, paper output, and color proofs, as well as scanning and other services.set-off:
When the ink of a sheet that has already been printed rubs off onto the next sheet.shadow:
The darkest parts of a photograph, represented by the largest dots in a halftone.sharpen:
To heighten the contrast between the dark and light tones of an image.sheet-fed:
A type of printing press that accepts paper in the form of sheets, as opposed to a web-fed press, which accepts paper in the form of webs, or rolls.sheetwise:
To print one side of the paper with one plate, then to turn the sheet over and print the other side with another plate but using the same gripper and side guide.short ink:
An ink that does not flow freely, as opposed to a long ink.short rate:
A reduction in the suggested retail price of less than 40%.short rate discount:
A reduction in the suggested retail price of less than 40%.short run:
A print run of less than 10,000.show-through:
An undesirable condition in printing in which the ink on one side of the paper is visible from the other side under normal lighting conditions.side guide:
A guide on sheet-fed presses that positions the sheet sideways as it feeds it into the front guides before entering the impression cylinder.side wire:
To wire the signatures of a magazine or booklet on the side near the backbone when binding.signature:
A group of pages brought together into proper order and alignment following folding.silhouette halftone:
A halftone with all screen background removed.silk screen:
A printing method in which ink is pushed through a stencil, used for imprinting T-shirts and heavier paper stocks.simultaneous edition:
Two different versions of a book published at the same time.simultaneous submission:
A manuscript or query letter that is sent to more than one publisher for consideration at the same time.single copy order:
When a bookseller orders only one copy of a book.sinkage:
The extra white space at the top of a chapter opener.six-color:
A printing process that uses six different colors, for example, the standard four-color process inks (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) plus two spot colors.six-up:
The imposition of six items to be printed on the same sheet in order to take advantage of full press capacity and minimize paper consumption.sizing:
A treatment for paper that gives it resistance to the penetration of liquids such as water.skid:
A platform that holds a pile of cut sheets in a printing plant.slipcase:
A hard case usually made of sturdy cardboard that holds a hardcover or softcover book so that the book's spine is showing.slitting:
The process of cutting printed sheets with a cutting wheel on press or on a folding machine.slug:
A short phrase or word that identifies an article as it goes through the production process; usually placed at the top corner of submitted copy.slush pile:
The pile of unsolicited manuscripts and query letters accumulated by a publisher.small caps:
A set of capital letters of a particular typeface made in the same height as the lowercase letters of the same face.Smythe sewn:
A form of binding in which the signatures are sewn together with thread before the cover is attached, usually used with hardcover books.snail mail:
To use the regular postal service instead of e-mail or fax to send documents from one person to another.soft copy:
The digital version of a manuscript or typeset copy before it is printed to paper.softcover:
A book bound with heavy paper, also called paperback or paperbound.soft dot:
A dot in photographic images that has excessive halation around its edges.soft hyphen:
A hyphen inserted into a word, using a specific command in a page layout program, that will not remain if the text happens to reflow.soft ink:
Ink that has the consistency of lithographic inks.soft proof:
A proof of an image or page layout on a computer monitor, as opposed to a hard proof, which is on paper of some other tangible substrate.soft return:
To create a new line ending, using a specific command in a page layout program, that will not remain if the text happens to reflow.sp:
Short for "spelling." A proofreader's mark used to signify that the spelling of a particular word should be checked.spec (noun):
Short for specification. The characteristics of typeset copy, such as typeface, point size, and leading, or the characteristics of a process color expressed in various percentages, or any set of specific instructions for reproducing an image or a page layout.spec (verb):
To determine and communicate the characteristics of typeset copy, color, or other aspects of a page layout.specification:
The characteristics of typeset copy, such as typeface, point size, and leading, or the characteristics of a process color expressed in various percentages, or any set of specific instructions for reproducing an image or a page layout.spectrum:
The complete range of colors, from blue (short wavelengths) to red (long wavelengths).spine:
The back of a bound book (hard- or softcover) that connects the two covers. Also called a backbone.spine out:
To display books on a shelf so that their spines are showing, as opposed to face out.spiral-bound:
A method of binding in which the book is held together with spiral wires inserted through holes punched along the inner margins of the pages.split run:
To divide a print run into two related jobs with minor variations, such as printing a portion of books in softcover and the other quantity of the same books in hardcover, or printing half the brochures in one color and the other half in another color.spot color:
A single solid (or screened) color printed using one separation plate, as opposed to a process color printed using two or more separation plates.spot illustration:
A small drawing, usually abstract, that provides graphic interest to an article or story that may not lend itself to other types of illustration such as photographs or charts.spot varnish:
a clear coating applied to a particular area of a printed piece that provides protection as well as a dull or glossy appearance, depending on the type of varnish.spread:
1. Two facing pages of a publication. 2. A trapping technique in which one color area is made slightly larger, used in conjunction with another trapping technique called a "choke," in which another color area is made slightly smaller to allow for misregistration on press.SRDS:
Standard Rate and Data Service. A reference used by advertising agencies to determine advertising rates and other statistics of various print and broadcast media.staging:
The process of preparing negatives and printing plates for printing. Also called stopping out.stat:
A photographic copy of type or art in the same size or a different size than the original; also known as a photostat.static neutralizer:
A printing press attachment that removes static electricity from the paper in order to avoid ink set-off and problems with the paper feeder.stay-flat binding:
A form of binding perfect-bound publications in which the cover spine is not actually glued to the edges of the bound pages so the book lays flatter when opened. Also called lay-flat binding.step-and-repeat:
The process of repeating an image or a group of images by "stepping" it into position using a predetermined measurement. This can be accomplished digitally in many page layout programs, or manually using photomechanics.stereotype:
A duplicate relief plate used in newspaper printing.stet:
Latin abbreviation of "let it stand." A proofreader's mark that means copy previously marked for correction should remain as it was.stiffness:
The ability of paper to resist bending and/or support its own weight.stochastic screening:
An alternative to conventional screening methods in which an image is color-separated using fine, randomly placed dots rather than geometrically aligned halftone dots.stock:
The type of paper or other material that will be used for printing.stopping out:
The process of preparing negatives and printing plates for printing, such as opaquing negatives and protecting certain areas of deeply etched plates. Also called staging.stream feeder:
A type of paper feeder that feeds several overlapping sheets of paper toward the grippers on a printing press.strike-on composition:
The process of setting type on composing machines or through direct impression, also called cold type.strip:
To position film negatives or positives on a flat (goldenrod) before platemaking.strip in:
To manually affix a film negative or positive to another piece of film.stripper:
A person whose job it is to position film negatives or positives on flats in preparation for platemaking.style guide:
A manual that outlines accepted usage of a corporate identity such as logos and letterheads, as well as the correct spelling of commonly used industry terminology.style sheet:
A system for a group of character attributes and paragraph formats that can be applied in one step to a paragraph or range of paragraphs.subhead:
A secondary line of text that appears after a headline, or a word or phrase that precedes a block of body text.subsidiary rights:
Additional rights that can be licensed to a publisher by the copyright owner for an additional fee, such as translation rights, television and movie rights, and electronic rights.subsidy press:
A publisher who charges the author to print the author's book, also called a vanity press.substance:
The weight in pounds of a ream (500 sheets) of standard size business papers. Similar to basis weight of other grades of paper.substrate:
The media on which something is printed, such as paper, vellum, cardboard, or cloth.subtitle:
A sentence or phrase that appears after the title of a book.subtractive color:
Color produced by using cyan, magenta, and yellow inks printed on white paper to absorb, or subtract, the red, green, and blue portions of the spectrum in the printing process.subtractive primaries:
Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (CMYK). The hues used for process color printing inks.sulphate pulp:
Paper made from wood pulps cooked in a sulphate solution. Also known as kraft.sulphite pulp:
Paper made from wood pulps cooked in a bisulphite solution.supercalender:
A stack or rolls used in papermaking to apply a high gloss finish on paper.suppress printout:
A command in page layout programs that allows the user to prevent an image or a page from printing.surprint:
To expose a second negative over a previously exposed negative.SWOP:
Specifications for Web-Offset Publications. A booklet that provides the web-offset specifications for separations, proofing, and printing process color in Europe.syndicate:
An organization that licenses and releases articles and stories for simultaneous release.syndication:
When a work is simultaneously licensed by and released to various media, such as newspapers or radio stations.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||